Laminated Construction
Acoustic glass typically consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with a specialized sound-control interlayer. This interlayer is designed to absorb and dissipate sound waves, reducing noise transmission.
Acoustic glass is specially designed laminated glass that reduces noise transmission. It consists of two or more glass layers with an acoustic interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or a specialized sound-dampening resin, which absorbs and dampens sound waves.
Thompson Innovative Glass manufactures Acoustic glass that is specially designed & engineered to reduce sound transmission, making it ideal for environments where sound insulation is important.
It is commonly used in buildings that may have high levels of noise pollutions surrounding it (busy highway, railways, airports, etc.) or applications needing sound privacy (medical, manufacturing, security, etc.)
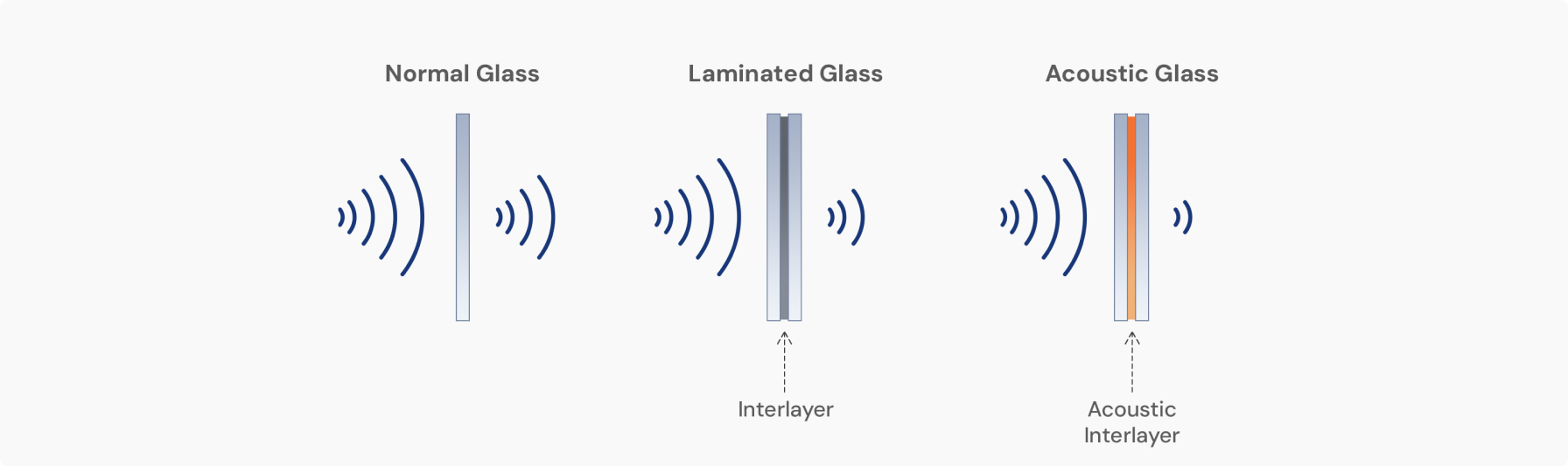
Acoustic glass typically consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with a specialized sound-control interlayer. This interlayer is designed to absorb and dissipate sound waves, reducing noise transmission.
Varying glass thicknesses in the layers of glass and the size of the airspace in an insulating glass unit can further disrupt sound waves, enhancing acoustic performance.
Despite its soundproofing properties, acoustic glass maintains high levels of transparency, making it suitable for applications where visibility is important.
The laminated glass make-up of acoustic glass plays a key role in reducing soundwaves into the structure.
The specialized interlayer in acoustic glass reduces the vibration of sound waves as they pass through the glass, lowering the sound transmission class (STC) rating.
Acoustic glass is particularly effective at reducing mid-to-high-frequency noise, such as traffic, voices, or industrial sounds.
Significantly decreases external noise, creating a quieter and more comfortable indoor environment.
Like standard laminated glass, the sound-control interlayer.will hold the glass together in post breakage scenarios, preventing glass shards from flying.
Available in various thicknesses, colors, and coatings (e.g., Low-E or solar control) to meet aesthetic and thermal performance building requirements.
Acoustic glass is specially designed laminated glass that reduces noise transmission. It consists of two or more glass layers with an acoustic interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or a specialized sound-dampening resin, which absorbs and dampens sound waves.
Acoustic glass blocks sound by using multiple layers and a noise-dampening interlayer to disrupt and reduce sound waves. This prevents noise from passing through, making spaces quieter.
Acoustic glass is effective against traffic noise, aircraft noise, construction sounds, voices, and other environmental disturbances.
Not exactly. Double glazing consists of two panes of glass separated by an air or gas-filled space, which provides some sound insulation. Acoustic glass, however, uses a special interlayer for superior noise reduction, making it more effective than standard double glazing.
Acoustic glass can reduce noise by up to 40–50 decibels (dB) depending on the thickness and composition. Standard double glazing typically reduces around 30–35 dB, while laminated acoustic glass offers higher sound insulation.
Acoustic glass typically has an STC rating between 35 and 50, depending on thickness and composition. The higher the STC rating, the better the sound insulation.
Yes. While standard laminated glass provides some sound reduction, acoustic laminated glass has a specially designed interlayer that enhances noise reduction, making it more effective than regular laminated glass.
Yes, but low-frequency sounds (such as bass from music or heavy machinery) are harder to block. Thicker glass and multi-layered acoustic glazing systems are more effective against low-frequency noise.
Yes, in many areas, acoustic glazing is required in noise-sensitive locations, such as near airports or busy roads, to meet building codes and noise mitigation standards.